IMAX3とllama.cppで実現するGUIチャット
我々のプロジェクト(LENZO)では、汎用アクセラレータIMAX上で大規模言語モデル(LLM)を動作させるにあたり、llama.cpp フレームワークのサーバー機能を中核に据えています。これにより、単なる性能評価にとどまらず、実用的なGUIチャット機能を構築しました。
English follows Japanese.
llama.cpp が提供するサーバー機能は、HTTP APIを通じてLLMの推論機能を提供します。これを用いて、GUIチャットアプリケーションを構築することができます。
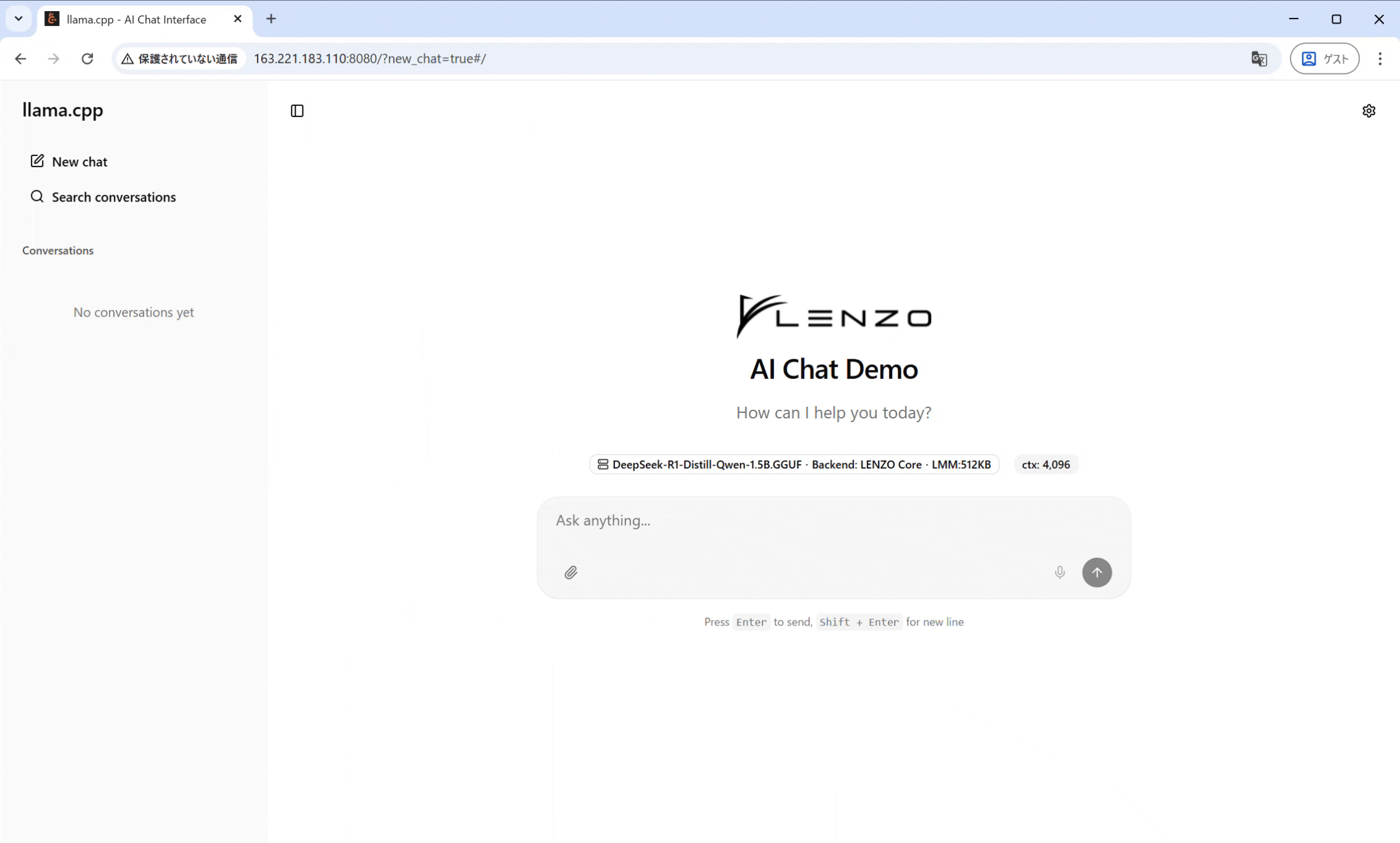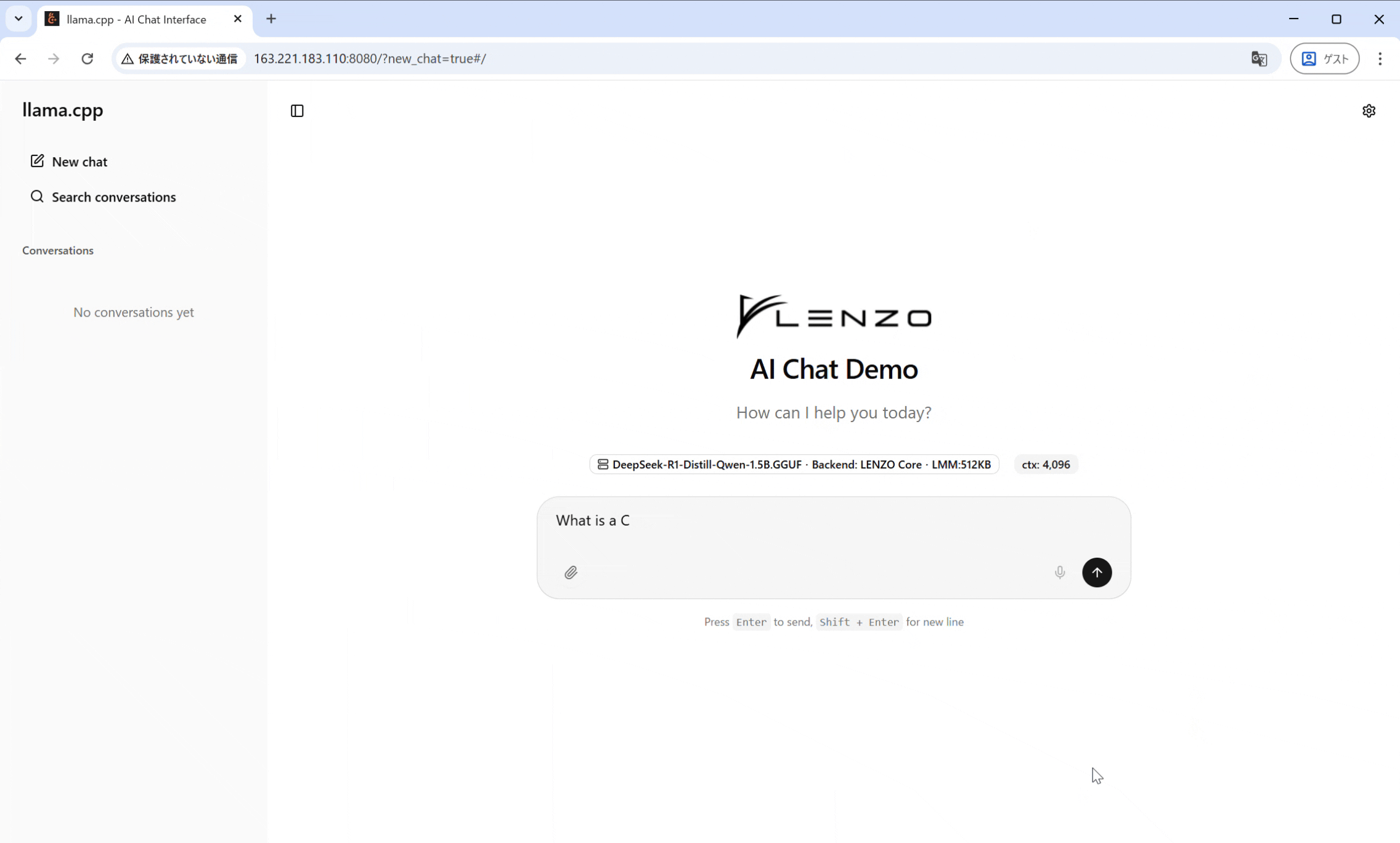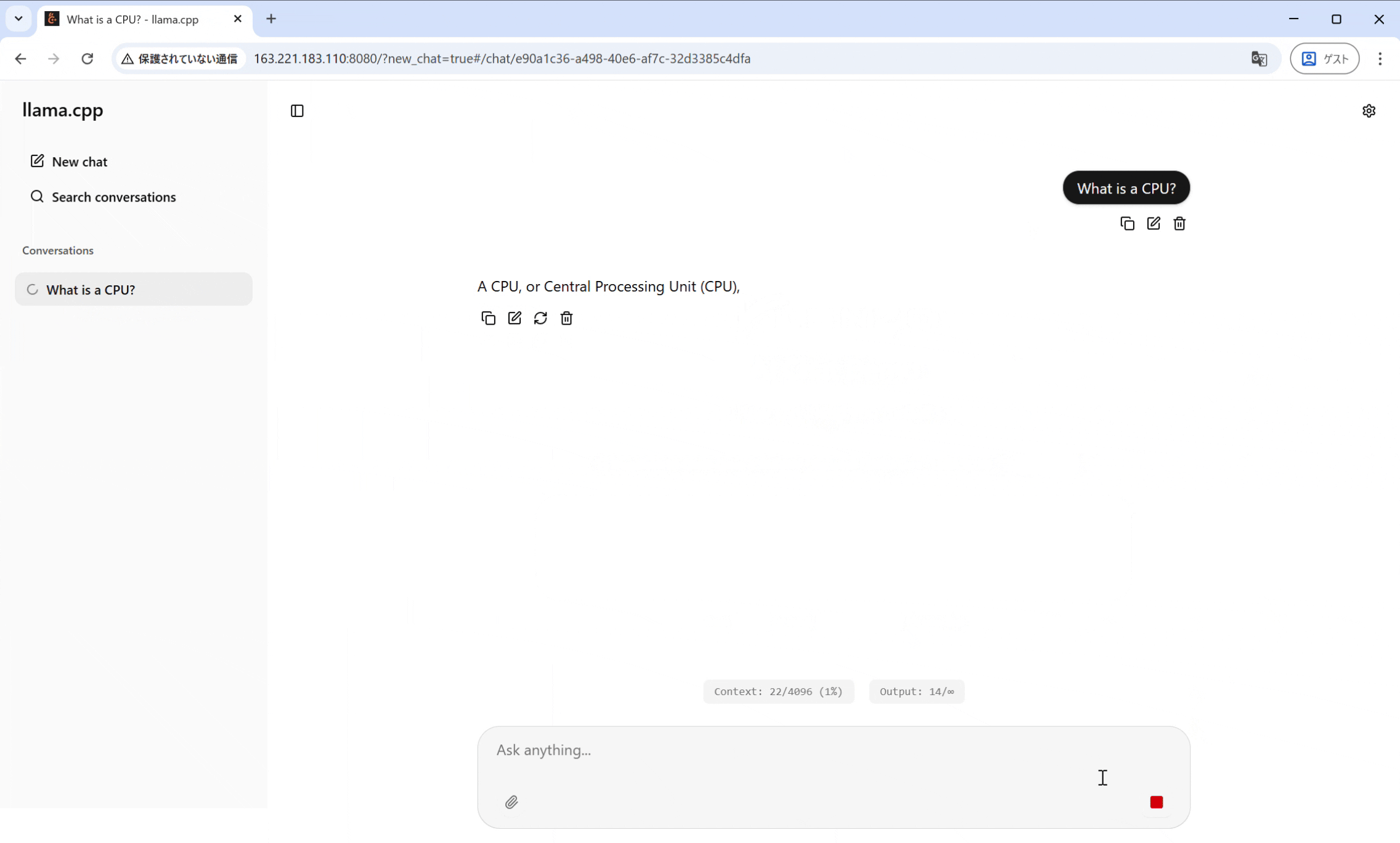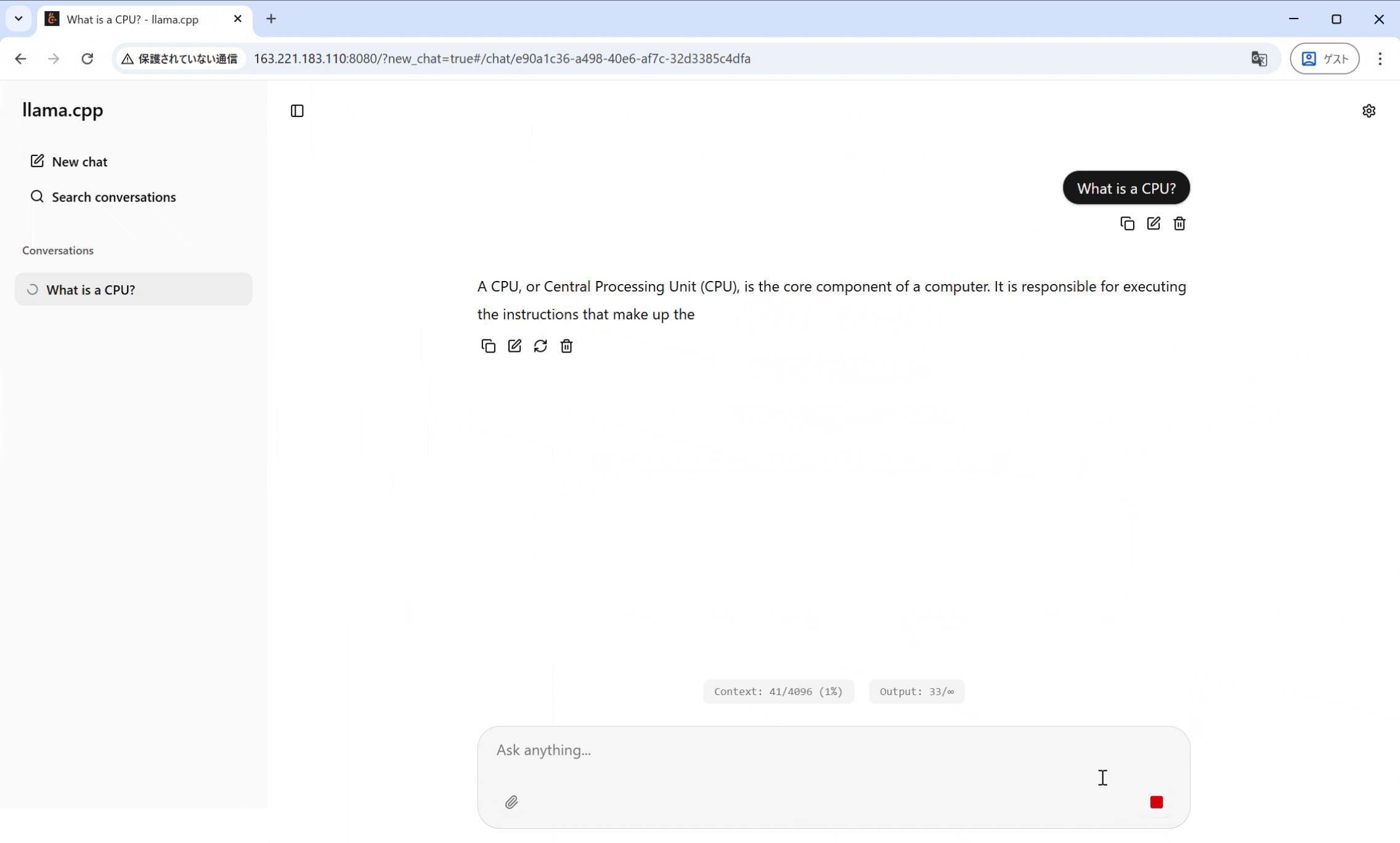
私は、奈良先端大コンピューティング・アーキテクチャ研究室のIMAX3 Host SoCでこのサーバーを稼働させ、そのAPIを利用するGUIチャットインターフェースを構築しました。これにより、ユーザーはWebブラウザなどから、電力効率の高いIMAXプラットフォーム上で動作するLLMと対話することが可能になります。
処理の役割分担: GUIサーバー と IMAXアクセラレータ
ホストCPUとIMAXアクセラレータが以下のように役割を分担しています。
- ホスト (ARM Cortex-A72プロセッサ)
- Linux OS上で
llama.cppサーバーを実行 - GUIからのHTTPリクエスト(チャット入力)の受付と応答。
- プロンプトのトークン化、KVキャッシュ管理、最終的なSoftmax演算など、複雑な制御やシーケンシャルな処理を担当。
- Linux OS上で
- IMAX (アクセラレータ)
llama.cppの CPUバックエンドプログラムを修正することで、推論のボトルネックとなる処理をIMAXが実行- GUIからのリクエストに基づき、Transformerの行列演算をオフロード実行。
- グループワイズで量子化された重みのデコード、行列演算、累算を効率的にパイプライン処理。
カスタム演算とデータ転送最適化
IMAXは、GGUFのQ8_0、Q2_K、Q3_K、Q6_K といった多様な量子化スキームに対応しています。
さらにIMAXのPE(Processing Element)は、OP_FML3 のようなカスタムALU操作(演算命令)を駆使します。これにより、量子化された重みのデコード処理を、演算パイプラインの途中でオンザフライで行うことが可能です。
さらに、PEとLMMを交互に配置するCGLAアーキテクチャと非同期実行、パイプライン化により、データ転送のオーバーヘッドを最小限に抑え、チャット応答のレイテンシを削減します。
E2E評価
多くの研究が理論的なピーク性能(TOPS/W)に注目する中、我々は llama.cpp サーバーを用いたGUIチャットという実用的なE2Eアプリケーションを通じて、システム全体の現実的な性能を評価しています。
28nm ASICプロセスへの性能予測では、IMAXはRTX 4090と比較しても高い電力効率(PDPで最大44.4倍、EDPで最大11.5倍改善)を示しています。
展望: Hugging Face エコシステムとの統合
今回の成果は、さらなる発展の可能性があります。
llama.cpp サーバーのAPIはOpenAI互換のものも提供されており、Hugging Faceなどの外部ツールとの連携も容易です。これにより、IMAXの強力なハードウェア性能を、広範なAI開発者コミュニティに提供できる可能性があります。
まとめ
IMAXプラットフォームは、「llama.cppサーバーがGUIからの対話を受け付け」「IMAX計算コアが重い推論処理を高速実行」「LMMとDMAがデータ転送を最適化する」という協調処理により、低消費電力で実用的なGUIチャット機能を実現しています。
GUI Chat Application with IMAX and llama.cpp
In our project, we use the llama.cpp server running on the IMAX3 Host SoC to provide a practical GUI chat application on top of a power‑efficient accelerator platform.
By exposing the LLM through an HTTP API, users can interact with the model from a web browser while the heavy computation is offloaded to IMAX.
Division of Responsibilities: GUI Server and IMAX Accelerator
The host CPU (ARM Cortex‑A72) runs Linux and executes the llama.cpp server.
It receives chat requests from the GUI via HTTP, performs tokenization, manages KV caches, and handles control‑intensive, sequential operations such as the final Softmax.
Meanwhile, the IMAX accelerator takes over the bottleneck matrix‑heavy parts of the Transformer, executing them efficiently in response to GUI requests.
This clear split of responsibilities allows the system to deliver responsive chat experiences while keeping power consumption low.
Custom Operations and Data Movement Optimization
IMAX supports multiple GGUF quantization schemes such as Q8_0, Q2_K, Q3_K, and Q6_K.
Its Processing Elements (PEs) use custom ALU operations like OP_FML3 to decode quantized weights on the fly as part of the compute pipeline.
By combining the CGLA architecture (alternating PEs and LMMs), asynchronous execution, and pipelining, the design minimizes data‑transfer overhead and reduces end‑to‑end response latency in chat.
End‑to‑End Evaluation
Rather than focusing only on theoretical peak performance (e.g., TOPS/W), we evaluate the system using a realistic end‑to‑end GUI chat application built on the llama.cpp server.
When projected to a 28 nm ASIC process, IMAX shows significantly better power efficiency than an RTX 4090 GPU, achieving up to 44.4× improvement in PDP and up to 11.5× improvement in EDP.
Outlook: Integration with the Hugging Face Ecosystem
The llama.cpp server offers OpenAI‑compatible APIs, making it easy to connect with external tools and ecosystems such as Hugging Face.
This opens the door for a wide range of developers to leverage IMAX’s hardware strengths through familiar, high‑level tooling and workflows.
Conclusion
By combining the llama.cpp server on the host, the IMAX compute cores for heavy inference, and optimized data movement through LMM and DMA, the IMAX platform delivers a practical, low‑power GUI chat experience.
This architecture demonstrates how tightly integrated hardware and software can bring state‑of‑the‑art LLM capabilities to energy‑efficient accelerator platforms.
